




- Race & Ethnicity
- Colonialism
- Settler Colonialism
- Ethnic Cleansing
- Genocide
- Apartheid
- Massacre
- Geneva Convention
- ICC
- Rome Statute
- Crimes against Humanity
- War Crimes
- Nakba
- Intifada
- Right to Armed Resistance
Race & Ethnicity
Race refers to the concept of dividing people into groups on the basis of various sets of physical characteristics and the process of ascribing social meaning to those groups.
Ethnicity describes the culture of people in a given geographic region, including their language, heritage, religion and customs (Washington University) (Britannica)
Colonialism
Domination of a people or area by a foreign state or nation: the practice of extending and maintaining a nation’s political and economic control over another people or area (Merriam Webster)
Settler Colonialism
Settler colonialism can be defined as a system of oppression based on genocide and colonialism, that aims to displace a population of a nation (oftentimes indigenous people) and replace it with a new settler population. (Cornell Law School)
Examples include Canada, the United States, Australia, and South Africa where the settlers remained
Non Settler Examples include India, Pakistan, Algeria, etc
Ethnic Cleansing
Ethnic cleansing, the attempt to create ethnically homogeneous geographic areas through the deportation or forcible displacement of persons belonging to particular ethnic groups. (Britannica). It’s about geographic areas and not necessarily about killing people
Genocide
Genocide, the deliberate and systematic destruction of a group of people because of their ethnicity, nationality, religion, or race. (Britannica). This is about extinguishing the race. Genocide is one way of ethnic cleansing. (UN describing Genocide)
Apartheid
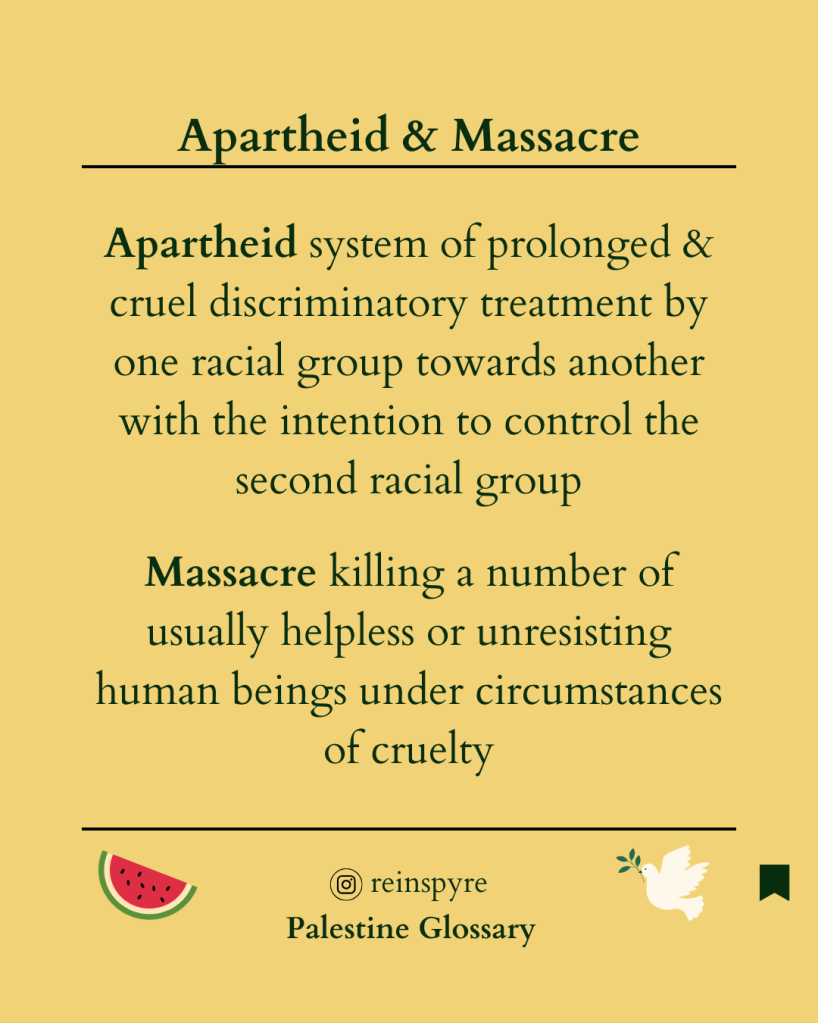
Apartheid can best be understood as a system of prolonged and cruel discriminatory treatment by one racial group of members of another with the intention to control the second racial group
Apartheid is a violation of public international law, a grave violation of internationally protected human rights, and a crime against humanity under international criminal law.
The term “apartheid” was originally used to refer to a political system in South Africa which explicitly enforced racial segregation, and the domination and oppression of one racial group by another. It has since been adopted by the international community to condemn and criminalize such systems and practices wherever they occur in the world.
The crime against humanity of apartheid under the Apartheid Convention, the Rome Statute and customary international law is committed when any inhuman or inhumane act (essentially a serious human rights violation) is perpetrated in the context of an institutionalised regime of systematic oppression and domination by one racial group over another, with the intention to maintain that system.
Massacre
The act or an instance of killing a number of usually helpless or unresisting human beings under circumstances of atrocity or cruelty (Merriam-webster)
Geneva Convention
Geneva Conventions, a series of international treaties concluded in Geneva between 1864 and 1949 for the purpose of ameliorating the effects of war on soldiers and civilians. Two additional protocols to the 1949 agreement were approved in 1977. (Britannica) (Geneva Convention document)
ICC
The International Criminal Court in The Hague prosecutes those accused of war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide.
In 1998, 60 countries signed the Rome Statute after it was opened for signature by the United Nations. The Statute laid the foundation for the establishment of the International Criminal Court in 2002. Its purpose is to investigate and prosecute war criminals. (ICC)
Rome Statute
The Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court is the treaty that established the International Criminal Court. It was adopted at a diplomatic conference in Rome, Italy on 17 July 1998 and it entered into force on 1 July 2002.
The Rome Statute, grants the ICC jurisdiction over four main crimes
- The crime of genocide;
- Crimes against humanity;
- War crimes;
- The crime of aggression
(ICC)
Crimes against Humanity
Crimes against humanity are acts committed as part of a widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, such as murder, deportation, torture and rape. The ICC prosecutes the perpetrators even if the crimes were not committed in times of war. (ICC)
Crimes against humanity have not yet been codified in a dedicated treaty of international law, unlike genocide and war crimes, although there are efforts to do so.
Article 7 of the 1998 Rome Statute establishing the International Criminal Court (Rome Statute) is the document that reflects the latest consensus among the international community on this matter.
For the purpose of this Statute, ‘crime against humanity’ means any of the following acts when committed as part of a widespread or systematic attack directed against any civilian population, with knowledge of the attack:
- Murder;
- Extermination;
- Enslavement;
- Deportation or forcible transfer of population;
- Imprisonment or other severe deprivation of physical liberty in violation of fundamental rules of international law;
- Torture;
- Rape, sexual slavery, enforced prostitution, forced pregnancy, enforced sterilization, or any other form of sexual violence of comparable gravity;
- Persecution against any identifiable group or collectivity on political, racial, national, ethnic, cultural, religious, gender as defined in paragraph 3, or other grounds that are universally recognized as impermissible under international law, in connection with any act referred to in this paragraph or any crime within the jurisdiction of the Court;
- Enforced disappearance of persons;
- The crime of apartheid;
- Other inhumane acts of a similar character intentionally causing great suffering, or serious injury to body or to mental or physical health.
War Crimes
War crimes include torture, mutilation, corporal punishment, hostage taking and acts of terrorism. This category also covers violations of human dignity such as rape and forced prostitution, looting and execution without trial. War crimes, unlike crimes against humanity, are always committed in times of war. (ICC)
Article 8 of the 1998 Rome Statute establishing the International Criminal Court (Rome Statute) is the document that reflects the latest consensus among the international community on this matter.
For the purpose of this Statute, ‘war crimes’ means:
- Grave breaches of the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, namely, any of the following acts against persons or property protected under the provisions of the relevant Geneva Convention:
- Wilful killing
- Torture or inhuman treatment, including biological experiments;
- Wilfully causing great suffering, or serious injury to body or health;
- Extensive destruction and appropriation of property, not justified by military necessity and carried out unlawfully and wantonly;
- Compelling a prisoner of war or other protected person to serve in the forces of a hostile Power;
- Wilfully depriving a prisoner of war or other protected person of the rights of fair and regular trial;
- Unlawful deportation or transfer or unlawful confinement;
- Taking of hostages
Nakba
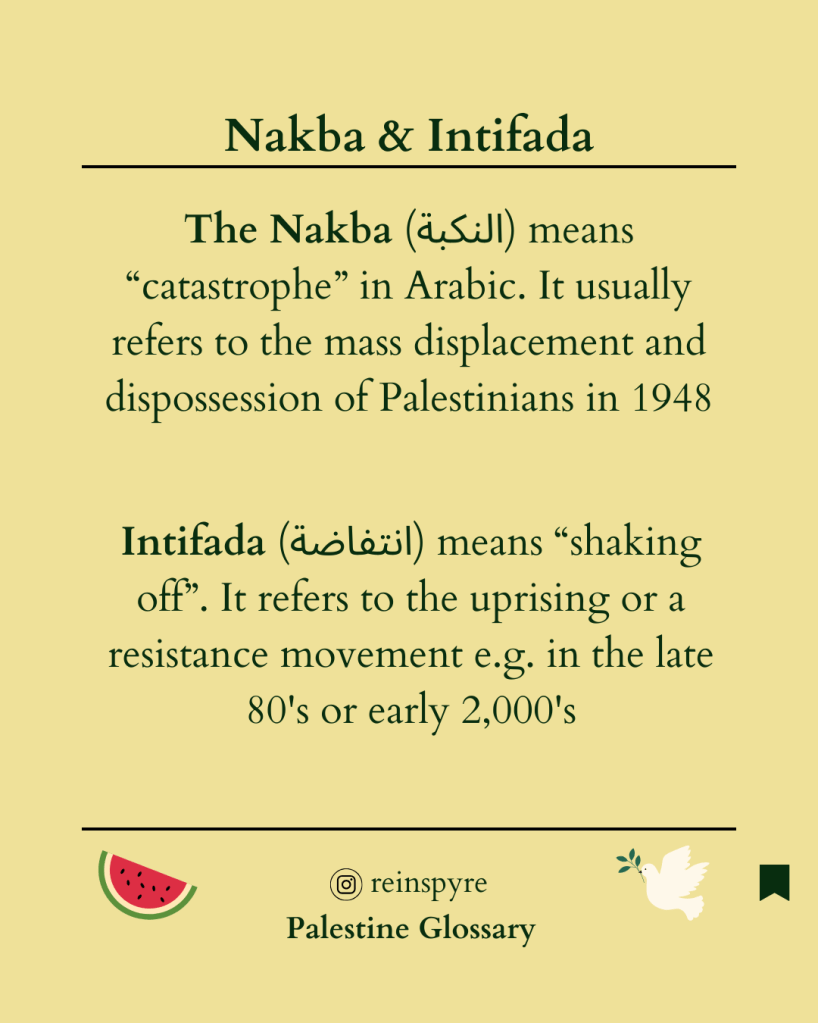
The Nakba (النكبة), which means “catastrophe” in Arabic, refers to the mass displacement and dispossession of Palestinians during the 1948 Arab-Israeli war. Before the Nakba, Palestine was a multi-ethnic and multi-cultural society. However, the conflict between Arabs and Jews intensified in the 1930s with the increase of Jewish immigration, driven by persecution in Europe, and with the Zionist movement aiming to establish a Jewish state in Palestine (United Nations on Nakba)
Intifada
Intifada ( انتفاضة) is an Arabic word which means “shaking off”. It refers to the uprising or a resistance movement. Intifada, either of two popular uprisings of Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza Strip aimed at ending Israel’s occupation of those territories (Britannica)
Right to Armed Resistance
According to UN General Assembly Resolution 45/130 quote “2. Reaffirms the legitimacy of the struggle of peoples for independence, territorial integrity, national unity and liberation from colonial domination, apartheid and foreign occupation by all available means, including armed struggle;” (UN GA resolution 45/130)
